The mobile app industry has evolved rapidly over the past decade, and businesses today are under constant pressure to deliver high-quality applications across multiple platforms in less time and at lower cost. This growing demand has made cross-platform mobile application development a preferred strategy for startups, enterprises, and product teams alike.
Rather than building separate applications for iOS and Android, businessesare now investing in cross-platform mobile app development frameworks that allow a single application to function seamlessly across devices. While this approach offers impressive cost and productivity benefits, it also introduces certain performance and technical trade-offs that must be carefully evaluated.
This blog explores the cost and performance trade-offs in cross-platform mobile app development, helping decision-makers understand when this approach is ideal and when native development may be a better fit.
What Is Cross-Platform Mobile App Development?
Cross-platform mobile application development is a software development approach where developers write a single codebase that can be deployed across multiple operating systems, primarily Android and iOS. Instead of maintaining two separate teams and projects, developers use specialized frameworks that translate the shared code into platform-compatible applications.
This model is also referred to as multi-platform mobile application development and is widely used by businesses that want faster releases and broader market reach. Popular frameworks such as Flutter, React Native, Xamarin, and Ionic provide tools, libraries, and APIs that allow developers to build apps that behave similarly to native ones.
The main idea behind cross-platform development is efficiency: maximizing output while minimizing development effort.
Cost Advantages of Cross-Platform Development

One of the strongest reasons businesses adopt cross-platform app development is the significant cost reduction it offers throughout the entire project lifecycle.
1. Reduced Development Costs
Since developers work with a single shared codebase, the overall development effort is drastically reduced. Businesses do not need separate iOS and Android teams, which cuts down on staffing, training, and coordination expenses. This approach can lower initial development costs by 30% to 50% compared to traditional native development.
For startups and small businesses, this cost efficiency makes it possible to enter the market with limited budgets while still offering apps on both major platforms.
2. Faster Time-to-Market
Cross-platform mobile app development allows businessesto release applications on multiple platforms at the same time. This speed is especially valuable in competitive markets where being first can determine success.
By avoiding duplicate development cycles, businesses can:
- Launch MVPs faster
- Gather user feedback earlier
- Iterate and improve more quickly
This faster deployment not only saves money but also accelerates revenue generation.
3. Lower Long-Term Maintenance Costs
Maintaining a single codebase is significantly easier than managing two separate native applications. Updates, bug fixes, and feature enhancements only need to be implemented once, reducing operational complexity and ongoing costs.
Over time, this makes cross-platform mobile application development far more economical for scaling products.
Performance Trade-Offs in Cross-Platform Apps
Despite its cost benefits, cross-platform development introduces some performance limitations compared to native solutions.
1. Slight Performance Overhead
Native apps are built using platform-specific languages like Swift and Kotlin, which provide direct access to hardware and system-level APIs. Cross-platform apps, on the other hand, rely on an abstraction layer that translates code into native components.
This extra layer can result in:
- Minor processing delays
- Slightly slower animations
- Higher memory consumption
For most business applications, such as e-commerce, social media, fintech, and productivity tools, these differences are barely noticeable. However, for performance-intensive apps like real-time gaming or 3D simulations, native development still offers superior results.
2. Delayed Access to New Platform Features
When Apple or Google introduces new operating system features, native developers gain immediate access through official SDKs. Cross-platform frameworks often take time to integrate these changes, meaning developers may have to wait before using the latest features.
This delay can be a drawback for businesses that rely heavily on cutting-edge device capabilities or frequent OS updates.
3. Platform-Specific UI Challenges
Each platform has its own design standards and user experience guidelines. While modern frameworks attempt to replicate native behavior, achieving perfect visual and interaction consistency across platforms can be challenging.
Some UI components may behave slightly differently, which can impact user experience if not carefully optimized.
Performance Comparison of Popular Frameworks
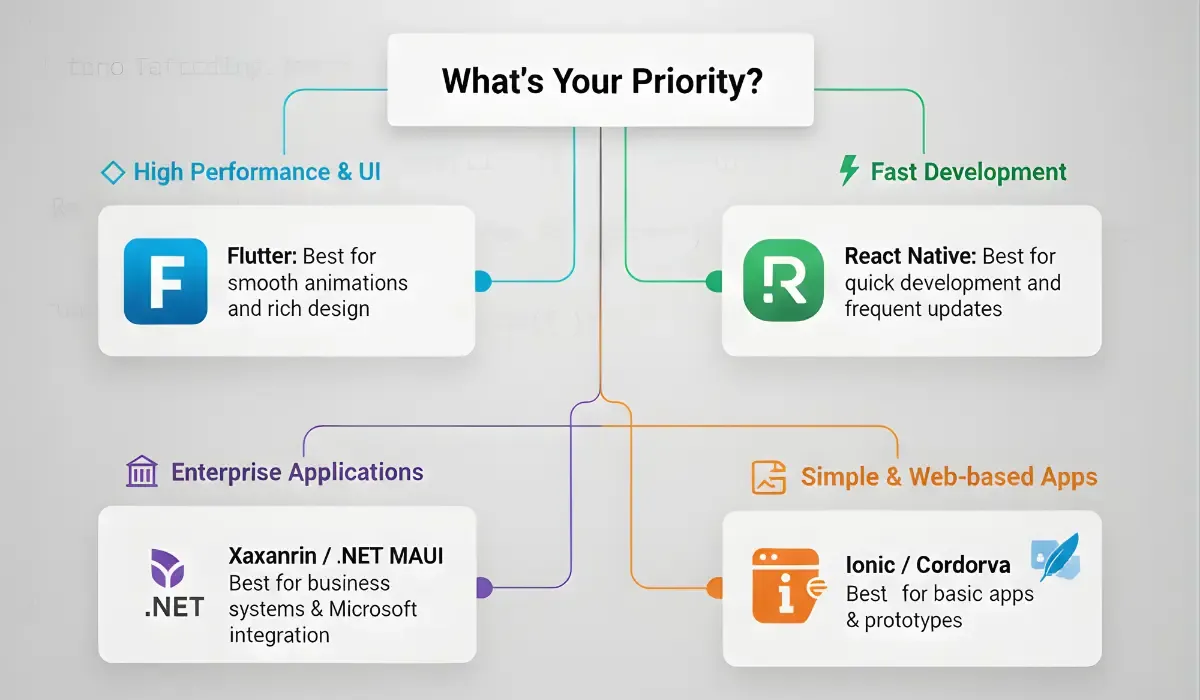
Different cross-platform app development frameworks offer varying levels of performance and flexibility.
React Native
React Native uses native UI components, making it one of the closest alternatives to native development. It provides strong performance for most applications and has a massive developer ecosystem.
It is ideal for projects that require quick development and frequent updates.
Flutter
Flutter compiles directly into native code and uses its own rendering engine. This results in excellent performance and smooth animations. It also ensures consistent UI across platforms.
Flutter is well-suited for apps that prioritize design and performance equally.
Xamarin / .NET MAUI
These frameworks are part of Microsoft’s ecosystem and are popular among C# developers. They offer good performance and strong integration with enterprise systems.
They are commonly used for enterprise-level applications.
Ionic / Cordova
These frameworks rely on web technologies and run inside a web container. While they are easy to develop and highly flexible, performance is noticeably lower compared to other frameworks.
They are best used for simple apps or prototypes.
When Cross-Platform Development Is the Best Choice
Cross-platform mobile app development is ideal when the goal is to maximize reach while minimizing cost and development time. It works best for:
- Startups building MVPs
- Business applications
- SaaS platforms
- eCommerce solutions
- Social networking apps
- Enterprise dashboards
In these scenarios, the slight performance trade-offs are outweighed by faster delivery and lower costs.
When Native Development Is More Suitable
Native development is still the better option for applications that demand maximum performance and deep system integration, such as:
- High-end gaming apps
- AR/VR experiences
- Real-time financial trading systems
- AI-powered image or video processing apps
These applications require low-level hardware access and highly optimized performance that cross-platform frameworks cannot fully deliver.
The Real Trade-Off: Cost vs Performance
The decision between native and cross-platform ultimately depends on your business priorities.
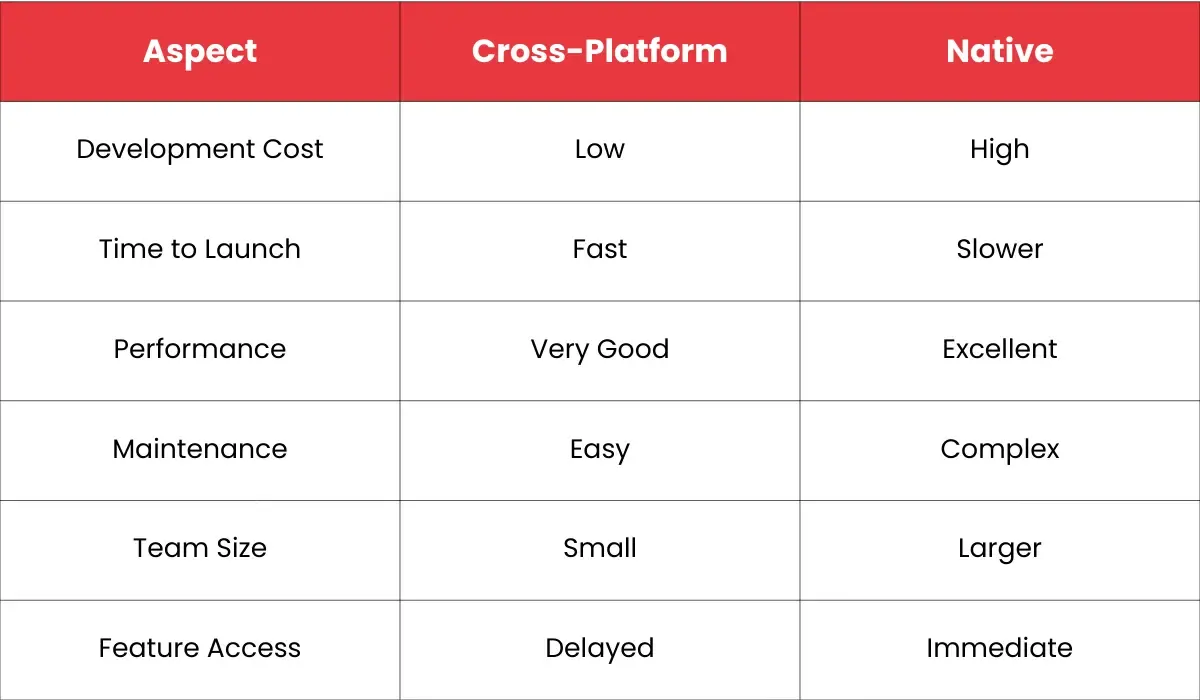
For most companies, multi-platform mobile application development offers the best balance between performance and affordability.
Final Thoughts
Modern cross-platform mobile app development frameworks have significantly improved in terms of speed, reliability, and user experience. What was once considered a compromise is now a mainstream development strategy adopted by global brands and tech startups alike.
Unless your application requires extreme performance or complex system-level functionality, cross-platform development provides a practical, scalable, and cost-effective solution.
In today’s competitive digital environment, cross-platform mobile application development is not just an alternative; it is often the smartest business decision.
FAQs
1. Is cross-platform mobile app development really affordable?
Yes. It is generally more affordable because developers create and maintain only one codebase for multiple platforms. This significantly reduces development, testing, and maintenance costs.
2. Which framework is best for cross-platform mobile app development?
There is no universal answer. Flutter is excellent for performance and UI, React Native is great for flexibility and community support, while .NET MAUI suits enterprise environments.
3. Can cross-platform apps access device hardware?
Yes. Cross-platform apps can access features like GPS, camera, sensors, Bluetooth, and biometrics through plugins and APIs.
4. Are cross-platform apps secure?
Security depends on implementation. With proper encryption, secure APIs, authentication, and compliance standards, cross-platform apps can be just as secure as native ones.
5. Is cross-platform suitable for enterprise applications?
Absolutely. Many enterprises use cross-platform solutions for internal systems, CRM tools, employee portals, and analytics dashboards.
6. What is the biggest disadvantage of cross-platform development?
The main drawback is limited performance for resource-intensive applications and delayed access to the newest operating system features.






