AI is developing at a pace never seen before. What was once limited to rule-based automation is now moving toward agentic AI, systems that can think, plan, decide, and act autonomously without constant human supervision. At the forefront of this evolution is Amazon Web Services (AWS), which offers a rich ecosystem that empowers developers and enterprises to build, deploy, and scale autonomous, intelligent systems.
In this blog, we will learn how to build Agentic AI on AWS, from fundamental services and key concepts to hands-on architectural patterns and real-world applications.
What Is Agentic AI?
Before diving into AWS agentic AI tools, it’s important to clarify what agentic AI means. Agentic AI describes AI systems that operate as autonomous agents, capable of:
- Observing their environment through data inputs;
- Planning a course of action using models or logic;
- Making decisions based on goals and constraints;
- Taking actions to achieve objectives;
- Adjusting strategies through feedback or reinforcement.
Unlike traditional models that simply respond to single queries (e.g., “classify this image”), Agentic AI systems pursue goals, manage context over time, adapt strategies, and act autonomously across complex workflows.
This evolution parallels the shift from scripts to services in software; AI is transitioning from static models to goal-driven agents.
Why Build Agentic AI on AWS Tools?
AWS has several advantages as a platform for building autonomous AI systems:
- Comprehensive AI/ML Stack: Pre-built models, training infrastructure, inference endpoints, and monitoring.
- Scalability: Elastic compute and serverless services that grow with demand.
- Security & Compliance: Integrated identity, auditing, and regulatory compliance capabilities.
- Integration: Seamless connection with event sources, databases, streaming data, and serverless pipelines.
- Managed Services: Reducing operational burden so teams can focus on business logic.
In short, AWS enables developers to build more complex and reliable systems.
What Are the Services Offered By AWS for Agentic AI Development
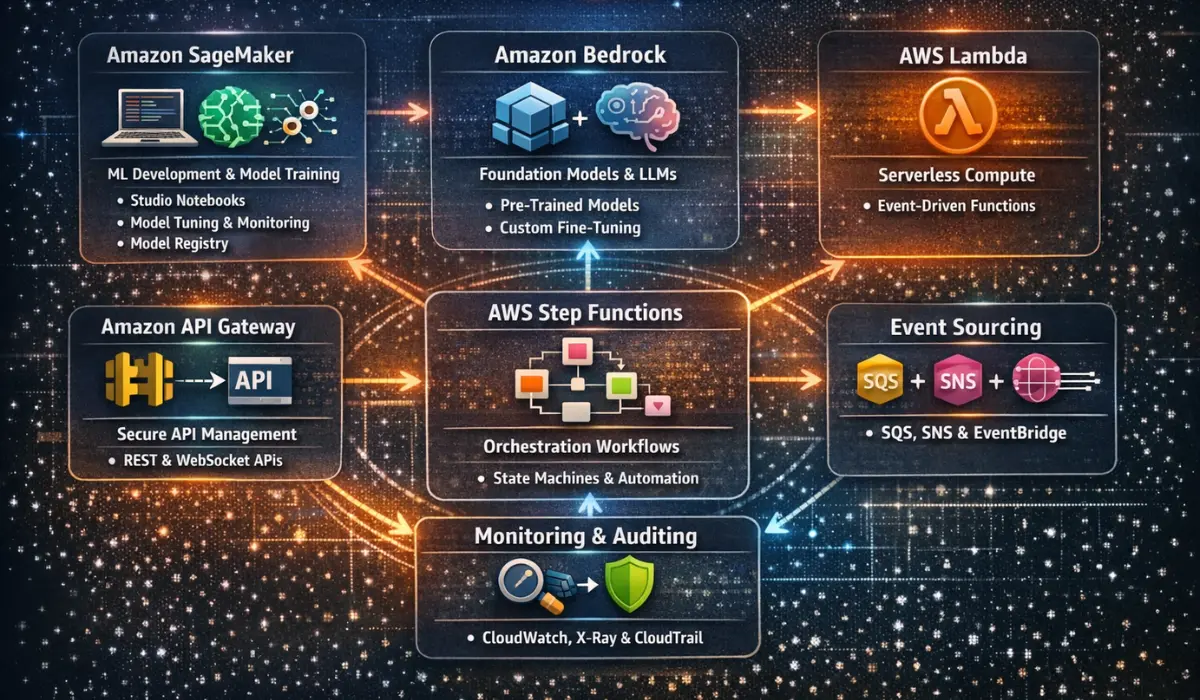
Here are the most relevant AWS agentic AI tools and services that collectively power autonomous systems:
1. Amazon SageMaker
Amazon SageMaker is AWS’s flagship machine learning platform. It supports the full ML lifecycle, from data preparation to model training, tuning, deployment, and monitoring.
Key SageMaker features:
- Studio Notebooks for interactive AWS AI agent development.
- Model Training & Hyperparameter Tuning with scalable compute.
- SageMaker Pipelines for ML workflows.
- Model Registry for version control and deployment governance.
- SageMaker Debugger to analyze training behavior.
- SageMaker Model Monitor to track drift and performance in production.
SageMaker provides the foundation for training the underlying models that power autonomous decision-making.
2. Amazon Bedrock
Amazon Bedrock is a fully managed service that provides access to powerful foundation models from AWS and leading AI partners (e.g., Anthropic, AI21, Cohere). It abstracts infrastructure complexities and makes it easy to integrate large language models (LLMs) into applications.
With Bedrock, developers can:
- Use pre-trained models to understand language, generate text, or embed semantics.
- Customize models with fine-tuning or retrieval augmentation.
- Access models via simple API calls without provisioning servers.
Bedrock is pivotal for creating reasoning engines and natural language interfaces- key components of many agentic systems.
3. AWS Lambda
AWS Lambda is a serverless service that executes code when triggered by events. It is ideal for tying AI logic into workflows, acting on triggers, and performing short, stateless tasks.
In agentic systems, Lambda functions often:
- Orchestrate decision logic.
- Execute task components.
- Invoke ML inference endpoints.
- Trigger follow-up events or notifications.
Lambda’s scalability and cost-efficiency make it attractive for event-driven AI systems.
4. Amazon API Gateway
Amazon API Gateway enables you to create and manage APIs that front AI services. It allows external clients or internal systems to interact with autonomous AI components securely.
Use cases include:
- Exposing agent interfaces to web/mobile apps.
- Building REST or WebSocket APIs for bidirectional communication.
- Managing authentication and throttling at the edge.
5. AWS Step Functions
AWS Step Functions provide visual workflows using state machines. They are excellent for defining multi-step agent processes, especially when decisions, branching, retries, and orchestrated activities are involved.
Example workflow components:
- Decision states (choice rules)
- Parallel tasks
- Integration with AWS services like Lambda, SageMaker, and SNS
- Long-running processes with wait and callback support
Step Functions bring clarity and resilience to complex AI automation.
6. Event Sources: SQS, SNS, EventBridge
Agentic systems thrive on events. AWS offers several eventing services:
- Amazon EventBridge for event buses and rule-based routing.
- Amazon Simple Queue Service (SQS) for message buffering and task queues.
- Amazon Simple Notification Service (SNS) for pub/sub notifications.
These services help decouple components and provide reliable asynchronous communication.
7. Monitoring & Auditing Tools
Observability is essential for production-grade agentic systems:
- AWS CloudWatch Metrics & Logs for performance and error tracking.
- AWS X-Ray for tracing distributed applications.
- AWS CloudTrail for audit trails and governance.
Together, these tools ensure reliability, operational visibility, and security compliance.
Building AI Agents on AWS: A Step-by-Step Example
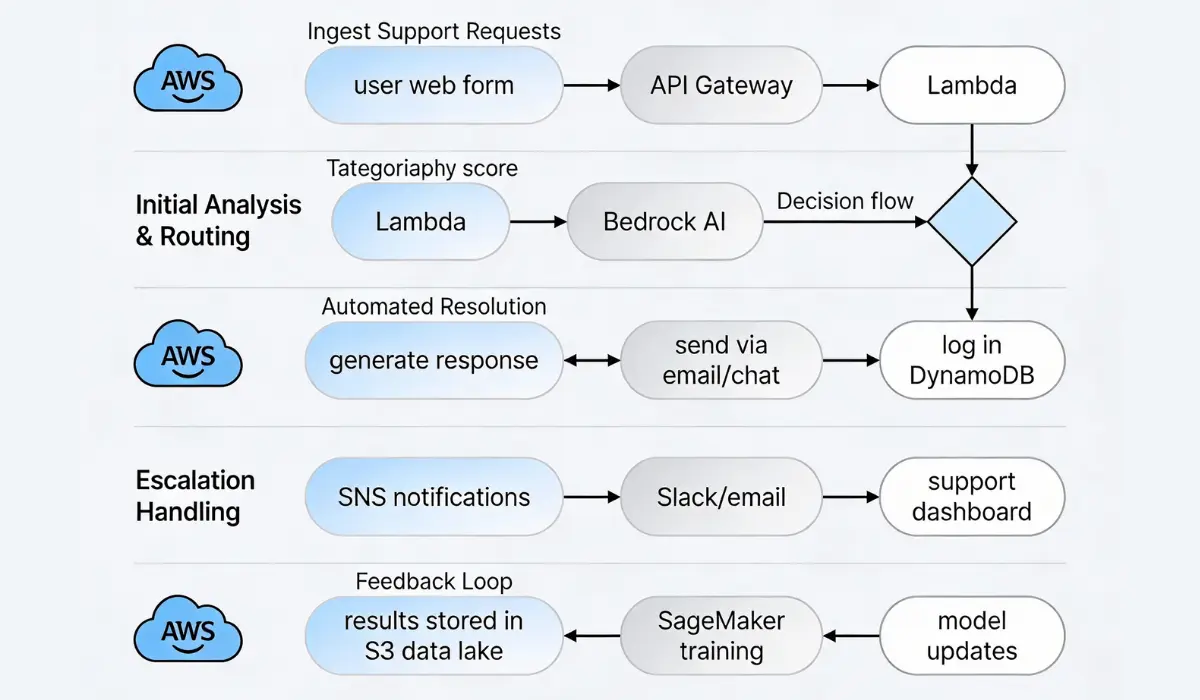
Let’s walk through a concrete example: an autonomous customer support agent that resolves tickets using AI and escalates only when necessary.
Step 1: Ingest Support Requests
- Users submit tickets via a web form.
- API Gateway processes the request and triggers the associated Lambda function.
Step 2: Initial Analysis & Routing
- Lambda sends ticket content to Bedrock for semantic understanding.
- Bedrock returns:
- Topic categorization
- Confidence score
- Suggested action
Based on confidence and category:
- If high confidence, proceed to automated resolution.
- If low confidence or a sensitive topic, escalate.
Step 3: Automated Resolution
- For resolvable tickets, Lambda crafts a response using Bedrock’s generation APIs.
- Lambda sends responses via email or chat integration.
- Resolution events are logged in DynamoDB.
Step 4: Escalation Handling
- Tickets flagged for escalation trigger SNS notifications.
- Support agents get alerts via Slack or email.
- Tickets are assigned and tracked in support dashboards.
Step 5: Feedback Loop
- When a ticket is closed, outcomes and agent feedback are stored in data lakes (S3).
- Periodic SageMaker training jobs refine the classification and response models.
This architecture leverages:
- API Gateway + Lambda for request/response
- Bedrock for NLP capabilities
- SNS for notifications
- DynamoDB/S3 for persistence
- SageMaker for ongoing learning
Architectural Patterns for AWS Autonomous AI Systems
Now, let’s look at typical architectural patterns when building agentic AI systems.
Pattern 1: Reactive Agent
This pattern is suitable for agents that react to inputs or events and make real-time decisions.
Flow:
- Event arrives via API Gateway or EventBridge.
- AWS Lambda processes the event.
- Lambda calls Bedrock or SageMaker inference for decision/context.
- Decision triggers downstream tasks (e.g., Lambda, SNS).
Ideal for:
- Chatbots
- Real-time classification
- Triggered automations
Pattern 2: Stateful Autonomous Workflow
For multi-step, time-bound goal-oriented tasks, AWS Step Functions helps manage state.
Flow:
- Client submits a job.
- Step Functions state machine orchestrates:
- Data validation
- Model inference
- Decision branches
- Messaging and updates
Ideal for:
- Complex automation pipelines
- Batch decisioning systems
- Long-running processes
Pattern 3: Continuous Learning Loop
Some agentic systems improve over time by incorporating feedback.
Flow:
- System logs decisions and outcomes in S3 or DynamoDB.
- Periodic training jobs in SageMaker use historical data.
- Updated models are versioned and deployed with SageMaker endpoints.
- API Gateway and Lambda invoke the latest models.
Ideal for:
- Recommendation engines
- Adaptive control systems
- Behavioral analytics
Best Practices for AI Agent Development on AWS

To maximize success, consider the following best practices:
1. Design for Failure
AWS autonomous AI systems should anticipate errors:
- Use retries and exponential backoff
- Implement fallbacks if ML inference fails
- Design workflows that can resume
AWS services like Step Functions and Lambda have built-in error-handling features that help.
2. Secure Your Agents
Security is critical:
- Use IAM Least Privilege
- Enable VPCs and private endpoints
- Encrypt data at rest and in transit
- Audit with CloudTrail
Agentic systems may operate autonomously, so the blast radius of misconfiguration must be minimized.
3. Monitor Behaviors Continuously
Beyond standard uptime metrics, monitor:
- Model drift
- Decision consistency
- Anomaly patterns
- Feedback loops
Use CloudWatch dashboards and alarms to capture subtle changes.
4. Ethical & Responsible AI
Autonomous AI can impact people seriously.
Consider:
- Bias mitigation during training
- Explainability of decisions
- Human-in-the-loop checkpoints where appropriate
By building guardrails, you reduce risks and increase trust.
Real-World Use Cases on AWS
AWS agentic AI systems are already transforming industries:
- Customer Support Automation: AI agents triage and respond to common inquiries, freeing human agents for complex tasks.
- Intelligent Process Automation: Back-office tasks like invoice processing, compliance checks, or workflow approvals can be fully automated with agentic logic.
- Operational Monitoring and Response: Systems can observe logs or performance data and autonomously resolve common issues, or escalate only when needed.
- Personalized Recommendation Engines: Autonomous agents analyze user behavior and optimize recommendations in real time.
Conclusion
Agentic AI systems represent the next frontier in intelligence automation. AWS offers a robust and mature ecosystem that enables developers to build, train, manage, and scale these systems effectively.
By combining AWS cloud AI services such as Bedrock, SageMaker, Lambda, Step Functions, and event streams, you can prototype and deploy autonomous agents that:
- Learn from data
- Make context-aware decisions
- Act with minimal supervision
- Adapt over time
Whether building intelligent virtual assistants, automated operational systems, or adaptive predictive models, AWS provides the tools and infrastructure to help realize your autonomous AI vision.
FAQ
1. What is the difference between Agentic AI and traditional AI?
Traditional AI systems typically respond to single inputs with predefined outputs (e.g., classification or prediction).
Agentic AI systems, on the other hand, are goal-driven and autonomous- they can plan, reason over time, make decisions, and take actions across multiple steps without constant human intervention.
2. Do I need to train my own models to build Agentic AI on AWS?
Not necessarily. You can start with pre-trained foundation models available through Amazon Bedrock.
For domain-specific or highly specialized use cases, you may fine-tune or train custom models using Amazon SageMaker.
3. Is Amazon Bedrock required for building agentic systems?
No, but it is highly recommended for language-based or reasoning-heavy agents.
You can build agentic systems using traditional ML models, rules, or even third-party APIs, but Bedrock simplifies access to powerful LLMs and generative models.
4. Is Agentic AI expensive to run on AWS?
It depends on scale and architecture. Using serverless services, batching inference, caching responses, and choosing the right models can significantly reduce costs. Many systems start small and scale only when the value is proven.