The future of business isn’t about automating a single, isolated task; it’s about automating an entire job function. While your competitors are still manually updating spreadsheets or relying on fragile, old-school scripts, the market leaders are deploying autonomous digital intelligence.
We are talking about sophisticated AI agents that can handle end-to-end workflows: reading a customer service ticket, checking internal knowledge for compliance, formulating a complex response, and updating the CRM, all without human oversight.
Your ability to compete depends on building a workforce that can actively think, learn, and make decisions at scale.
To start, you don’t need a massive data science team. What you need is this guide that explains how our five-step blueprint will help you build AI agents for business automation.
The Four Core Abilities of an AI Agent

Before we jump into the steps, what exactly separates a smart AI agent from a standard script or chatbot? It comes down to four critical abilities that make them autonomous:
- They Can See (Perception): They read and understand data from all kinds of inputs, including emails, system reports, and database entries.
- They Can Think (Reasoning): They interpret context, apply business logic, and figure out the best plan to solve a problem.
- They Can Act (Action): They interact with your other software, sending an email, updating a record in your database, or approving a payment, to execute their plan.
- They Can Get Smarter (Learning): They use machine learning to constantly check their work, learn from mistakes, and improve their strategy over time.
This capacity for autonomous, goal-oriented work is why AI agents are so powerful. Ready to start building AI agents? Let’s dive into the blueprint.
Also Read: Real Cost of Building an AI Agent
How to Build AI Agents from Scratch
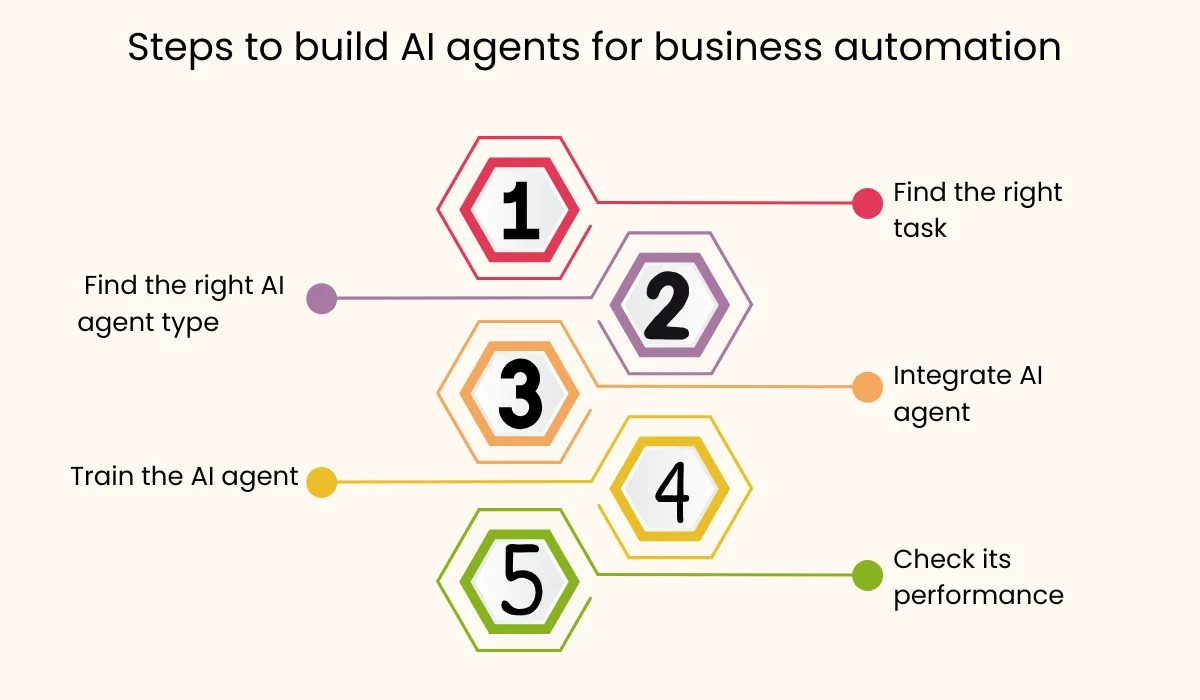
Moving from the drawing board to real-world business impact requires a clear path. Here is the five-step plan to successfully introduce, train, and deploy AI agents for business process automation.
Step 1: Find Your Time-Wasting Tasks
The first step is the most critical: picking the right task. The perfect job for an AI agent is one that is currently eating up your team’s time and has three main features:
- It’s Repetitive: It happens over and over again (daily, weekly, monthly).
- It’s Time-Consuming: It keeps valuable human employees tied up.
- It’s Rule-Based, but Needs Context: It follows clear business rules but requires a tiny bit of human judgment or context (like sorting emails, choosing the right person to route a ticket to, or creating standard monthly reports).
A Quick Tip: Run a quick audit across your departments. Ask your teams to track their time and simply label their work as “Creative/Strategy” or “Busywork/Admin” for one week. The “Busywork” column shows you exactly where to start. We suggest beginning with one small, low-risk task, like automatically classifying support requests, to prove the concept before you tackle critical systems.
Step 2: Find the Right AI Agent Type
Not all autonomous AI agents are built the same. The task you picked in Step 1 will tell you what kind of agent is best:
- Conversational Agents (Chatbots): These are best for talking directly with people (your customers or your employees). They handle questions and answers (Q&A), information lookups, or simple transactions like resetting a password.
- RPA Bots (Robotic Process Automation): These are perfect for jobs where the bot has to click, copy, and paste on a user interface or work with older systems. They are great for moving data between systems. Modern RPA is getting smarter, evolving into Intelligent Automation.
- Decision-Making Agents: These work in the background. They look at huge amounts of data to make strategic choices, like detecting fraud, figuring out the best price for a product, or managing complex inventory. They usually run invisibly inside your existing software.
Choosing the right tool ensures you get the biggest return on your investment.
Also Read: How to Create AI Agent Workflows for Enterprise-Grade Automation
Step 3: Make Sure AI Agents Can Talk to Your Existing Systems
An autonomous AI agent can’t help your business if it can’t interact with your business software. For example, a finance agent is useless if it can’t check budget limits in your ERP (Enterprise Resource Planning) system or update a sales lead’s status in your CRM (Customer Relationship Management) system. So, make sure the agent has these key connections.
The Key Connections:
- API Connectors: You need secure, reliable ways to connect the agent to your CRM (like Salesforce or HubSpot) and your core databases.
- Email and Messaging Hooks: This allows the agent to watch your inboxes, quickly categorize messages, and reply to basic communication.
- Internal Knowledge Bases: This is the agent’s “brain.” It needs access to all your company’s technical manuals, internal policies, and procedures to give smart, accurate answers.
Connecting the agent makes it active; it stops being a passive piece of AI and starts triggering real, necessary business actions.
Step 4: Make the AI Agent Smart
AI agents rely on two kinds of knowledge: the general knowledge they came with (from their underlying model) and the specific, unique data of your company. Training is essential to make the agent a reliable expert in your business processes.
- Contextual Grounding (RAG): You must feed the agent your company’s internal documents, records of past customer conversations, standard guides (SOPs), and product information. This process,often called Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG),makes sure the agent’s answers are compliant, accurate, and completely relevant to your specific context.
- Training for Mistakes: Teach the agent what not to do. Show it examples of bad customer responses or attempts at fraud so it learns the boundaries.
- Simple Feedback Loops: Always give your human operators an easy way to give the agent a quick thumbs-up or thumbs-down on its work. This small, continuous flow of human feedback is absolutely vital for the agent to keep improving.
Step 5: Monitoring and Continuous Improvement
Launching the agent isn’t the end; it’s just the beginning of its learning cycle. Autonomous AI agents need constant monitoring and improvement.
Tracking Performance (KPIs): You need to measure success. Track things like:
- Automation Rate: What percentage of tasks did the agent handle completely without a human needing to step in?
- Accuracy Rate: How often were the agent’s decisions or answers correct compared to human verification?
- Speed: How fast does the agent finish the job compared to a human?
Watching for Issues (Anomaly Detection): Use monitoring tools to alert you when the agent does something unexpected. A sudden drop in accuracy might mean a system error or a gap in its training data.
Scheduled Retraining: Plan regular sessions (say, once a month) to look closely at all the mistakes the agent made. Correct those mistakes and feed the corrected data back into the agent’s training set. This keeps the machine learning loop strong and ensures the agent evolves alongside your business.
Also Read: How to Test an AI Agent
What Are the Best AI Agent Building Platforms?

You don’t need to hire a massive data science team to get started. Modern development tools have made AI agent creation much easier:
- Microsoft Copilot: If your company heavily uses Microsoft products (Azure, 365), Copilot is an integrated conversational agent built right into those apps. It lets employees quickly draft documents, summarize meetings, or even write simple code based entirely on your company’s private data.
- LangChain: This is a very popular open-source framework. It gives developers the essential pieces needed to build multi-step AI agents. It lets you “chain” together things like language models, prompt templates, and tools that connect to outside systems. Developers use this for maximum control over how the agent thinks and acts.
- Google Dialogflow: A robust platform specifically for building ready-to-use conversational AI agents. It has excellent natural language understanding and makes it simple to plug the agents into websites, mobile apps, or voice systems.
- Rasa: Another strong, open-source tool focusing on conversational AI assistants that are great at handling complex, evolving conversations and connecting deep into enterprise software.
What all these AI agent builders share is the ability to connect the agent’s core brain (the LLM) to external data and systems; that’s the key to making the agent an active worker.
What Are the Benefits of Building an AI Agent for Business Automation?
At the end of the day, every business investment is about the Return on Investment (ROI). The case for AI agents is incredibly strong and focuses on two major areas:
- Saving Money and Boosting Efficiency: By completely automating frequent, repetitive tasks, you drastically cut down on the human hours previously spent on admin work. This means your expensive, skilled human employees are free to focus only on high-value work that requires creativity, empathy, and strategic thinking. Plus, agents never get tired, work without errors 24/7, leading to massive increases in throughput.
- Driving Revenue and Improving Quality: AI agents tailored for business automation make your work consistent (e.g., ensuring every contract review follows the same high standard) and instantly improve customer experience (e.g., providing fast, accurate support). Smart predictive agents also make sales and marketing much better by instantly finding the most likely customers and optimizing spending.
Conclusion
Looking to the future, the next big step is the rise of truly autonomous AI agents in businesses. These systems won’t just follow a set of steps; they will dynamically figure out their own plans and break down large goals, like “Launch a new marketing campaign,” into smaller, executable tasks. This level of hyperautomation promises to change the very structure of work, where AI agents handle the bulk of operations, allowing humans to step fully into roles of strategy and innovation.
Looking to build AI agents or deploy pre-built ones? We’ve got you covered with our AI agent development services.
FAQs
- What is an AI agent in business automation?
An AI agent is a software program that uses artificial intelligence to perform tasks autonomously, such as answering customer queries, processing data, or making decisions based on business rules. - How is an AI agent different from traditional automation tools?
Traditional automation follows fixed rules, while AI agents learn from data, adapt to changes, and make intelligent decisions without constant human intervention.
- What business processes can AI agents automate?
Common areas include customer support, invoice processing, HR onboarding, lead qualification, and supply chain management. - Do I need coding skills to build AI agents?
Not always. Many platforms like Microsoft Copilot, Dialogflow, and Rasa offer low-code or no-code options for building AI agents. - How long does it take to deploy an AI agent?
It depends on complexity. Simple chatbots can be deployed in days, while advanced decision-making agents may take weeks for data preparation, training, and integration. - Are AI agents secure for business use?
Yes, if implemented with proper data privacy measures, encryption, and compliance with regulations like GDPR. - What is the cost of building AI agents?
Costs vary based on complexity, data requirements, and integration needs. Some platforms offer subscription models, while custom solutions may require a higher upfront investment.







