When most people think about software development, they picture mobile apps, web platforms, SaaS tools, or enterprise systems. These forms of software are visible, interactive, and user-driven. However, there is another category of software that quietly runs the modern world without most people ever noticing it- embedded software development.
From automobiles and medical devices to smart appliances, industrial machinery, and aerospace systems, embedded software is everywhere. Yet, despite sharing the word “software,” embedded systems software development is fundamentally different from app development in philosophy, process, tools, and responsibilities.
To truly understand how software development for embedded systems differs from building applications, we must explore how embedded software is designed, how it interacts with hardware, and why its constraints shape every technical decision.
Why Is Hardware the Core of Embedded Software Development?
The most fundamental difference between app development and embedded software development is the role of hardware.
In traditional app development, hardware is abstracted away. Whether you are building a mobile app or a web platform, you assume that the operating system will manage memory, processing power, networking, and device drivers. Developers mainly focus on user experience, business logic, and data flow.
In embedded systems software development, hardware is not hidden; it is the foundation of everything. The software exists specifically to control or interact with a physical device. Every embedded project starts with hardware-related questions:
- What processor is being used?
- How much memory is available?
- Which sensors and peripherals are connected?
When you develop embedded systems, your software is tightly coupled to the electronics. Changing the hardware often means rewriting large portions of the software. This close relationship makes software development embedded far more complex than app development.
Embedded developers must understand microcontrollers, registers, memory maps, I/O pins, and communication protocols. This is why embedded software development is considered both a software and a hardware discipline.
Why Are Resource Constraints So Critical in Embedded Systems?
One of the biggest differences between app development and software development for embedded systems is the availability of resources.
In app development, developers have access to powerful hardware. Smartphones have gigabytes of RAM, multi-core CPUs, and fast storage. Cloud platforms scale almost infinitely. Performance issues are often solved by adding more resources.
In embedded software development, resources are extremely limited. Many embedded devices operate with only a few kilobytes of memory and very low processing power. Some systems do not even have a file system.
This forces developers to write highly optimized code. When you develop embedded, you must think carefully about:
- How much memory does each function uses
- How many CPU cycles does an algorithm consumes
- How often are tasks execute
In software development for embedded systems, inefficiency is not just a performance problem; it can cause the entire device to crash. That is why embedded developers work closely with hardware, using languages like C and C++, where memory and execution are fully under their control.
Why Does Real-Time Behavior Matter More Than Features?
In most applications, timing is flexible. If an app responds in half a second instead of instantly, users may complain, but the system still functions.
In embedded systems software development, timing is often critical to correctness and safety.
Many embedded systems are real-time systems, meaning they must respond within strict time limits. Missing a deadline is not acceptable. The system is considered broken if it fails to act on time.
For example, in automotive systems, braking, airbag deployment, and engine control must happen within precise time windows. In medical systems, pacemakers and infusion pumps must operate at exact intervals. In industrial automation, machines must react immediately to sensor input.
This is why software development embedded focuses heavily on deterministic behavior. Developers must ensure that tasks execute within predictable time bounds. Real-time operating systems or bare-metal scheduling are commonly used to meet these requirements.
Unlike app development, where performance is about speed and responsiveness, embedded software development treats timing as a core functional requirement.
Which Systems Do Embedded Systems Interact With?
Another major difference lies in what the software interacts with.
Apps mostly interact with digital elements such as users, servers, databases, and APIs. Even when they use hardware features like cameras or GPS, these are heavily abstracted.
In embedded software development, the software interacts directly with the physical world. It reads real-world signals from sensors and controls physical components through actuators.
When you develop embedded systems, your software may be responsible for:
- Measuring temperature or pressure
- Controlling motors and valves
- Managing electrical power
- Monitoring physical movement
This means software development in embedded systems must deal with noise, signal distortion, hardware failures, and environmental conditions. Developers must understand how physical systems behave and how to compensate for inaccuracies.
This is why embedded development often requires knowledge of physics, electronics, and control systems, making it fundamentally different from app development.
Why Do Many Embedded Systems Run Without a Full Operating System?
App development is built on top of powerful operating systems like Android, iOS, Windows, or Linux. These platforms manage memory, security, networking, file systems, and multitasking.
In embedded software development, many systems do not use a full operating system. Some run on a lightweight real-time operating system, while others run on bare metal without any OS at all.
When you develop embedded, you may need to manage:
- Memory allocation manually
- Task scheduling
- Interrupt handling
- Peripheral drivers
There is no safety net. If your code fails, the entire system may crash with no error message and no recovery.
This low-level nature makes software development embedded closer to systems programming than application programming. Developers must understand how the processor works internally and how software maps directly to hardware behavior.
What About Debugging?

Debugging is one of the most painful differences between these two fields.
In app development, debugging is convenient. Developers have access to advanced debuggers, detailed logs, simulators, and testing environments.
In embedded systems software development, debugging often requires specialized hardware tools. These include in-circuit debuggers, logic analyzers, and oscilloscopes.
Sometimes the only way to debug is to observe physical signals or blinking LEDs. There may be no screen, no logs, and no user interface at all.
This makes embedded software development slower and more demanding. Developers must be extremely methodical and understand both software behavior and electrical signals.
Why Is Power Management a Design Requirement?
Power consumption is rarely a primary concern in app development. Smartphones and computers are designed to handle power management automatically.
In software development for embedded systems, power efficiency is often one of the main design goals.
Many embedded devices are battery-powered or energy-constrained. When you develop embedded systems, your software directly controls how much power the device consumes.
This includes managing sleep modes, clock speeds, sensor activation, and communication cycles. A poorly designed system can drain a battery in days instead of years.
This makes embedded sw development fundamentally different from app development, where the operating system largely handles power management.
Why Are Updates and Maintenance So Difficult?
Apps are easy to update. Developers can push fixes and features daily through app stores or cloud deployments.
Embedded systems are much harder to update. Many devices are deployed in remote locations, operate offline, or must meet strict regulatory requirements.
Once you develop embedded software, it may run unchanged for decades. Bugs are not just inconvenient; they can be permanent and extremely expensive to fix.
This is why embedded systems software development prioritizes reliability and long-term stability over rapid iteration.
Why Does Embedded Software Require Certification and Compliance?
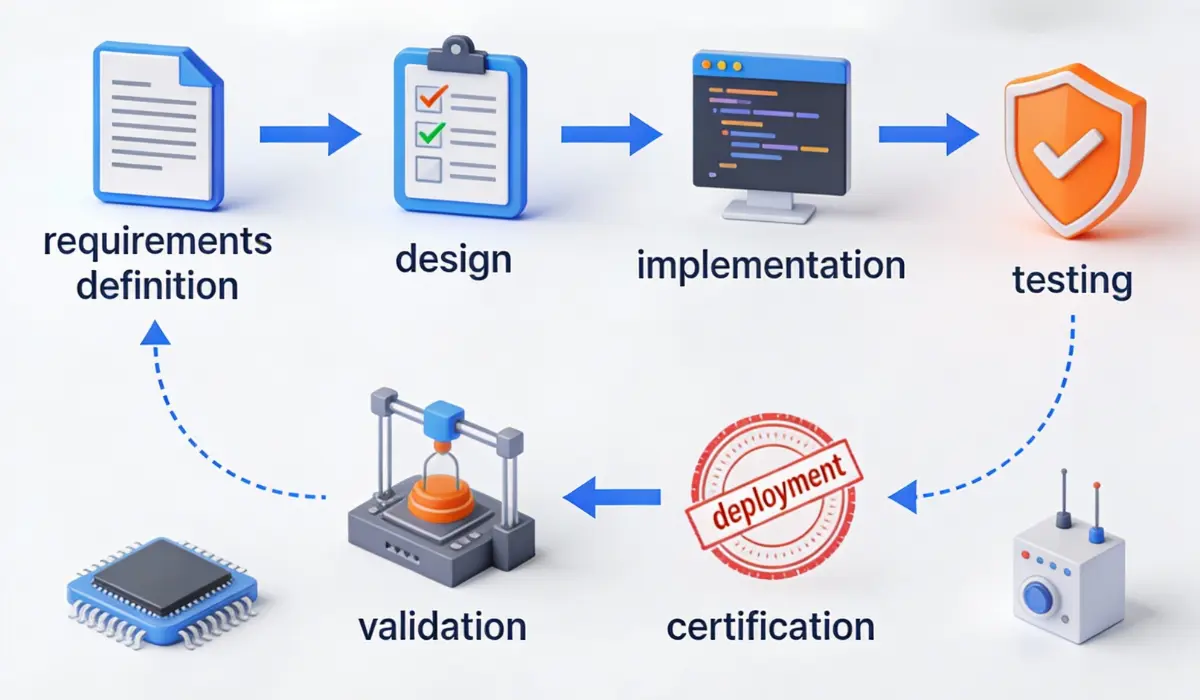
Most apps are lightly regulated. Even serious bugs rarely have legal consequences.
In embedded software development, many systems must comply with international safety and quality standards. These include automotive, medical, industrial, and aerospace regulations.
This means software development embedded involves extensive documentation, testing, and validation. Every feature must be traceable, verified, and justified.
The development process is slower, but it ensures safety, reliability, and legal compliance, something rarely required in app development.
Conclusion
Although both involve writing code, embedded software development and app development are fundamentally different disciplines.
App development focuses on users, interfaces, and rapid delivery.
Embedded development focuses on hardware, real-time behavior, and physical reliability.
When you develop embedded systems, you are not just building software; you are engineering machines that interact with the real world under strict constraints.
That is what truly makes software development in embedded systems fundamentally different from app development. It is not simply another branch of programming; it is a unique form of engineering where software and hardware become one system.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
-
What is embedded software development?
Embedded software development is the process of building software that runs on dedicated hardware devices to control or monitor physical systems.
-
How is embedded systems software development different from app development?
It focuses on hardware interaction, real-time performance, and limited resources, while app development mainly focuses on user interfaces and business logic.
-
Is embedded software development harder than app development?
Yes, because it requires both hardware and software knowledge, works under strict constraints, and often involves real-time and safety-critical systems.
-
Does embedded software need an operating system?
Not always. Some systems run on bare metal, while others use lightweight real-time operating systems.
-
What services does Softude offer in embedded software development?
Softude provides firmware development, system integration, real-time solutions, IoT development, and embedded product engineering.
-
Can Softude help with legacy embedded systems?
Yes, Softude helps modernize legacy systems by improving performance, adding connectivity, and upgrading firmware.
-
Why choose Softude for embedded software development?
Softude offers strong technical expertise, industry experience, and end-to-end support for embedded systems development.






