Artificial Intelligence has come a long way, from handling simple, isolated tasks to managing complex processes on its own. At the center of this shift are intelligent agents, AI systems that can reason, make decisions, and interact with other agents, tools, or even humans.
For these agents to work effectively, they need well-structured workflows that clearly define how tasks are carried out, decisions are made, and outputs are produced. In other words, an AI agent workflow is a roadmap that guides an agent step by step toward completing a task.
The challenge, of course, lies in designing these workflows. Done right, they make agents efficient, reliable, and scalable. In this blog, we’ll explore exactly how to design, orchestrate, and optimize AI agent workflows so you can get the most out of your AI systems.
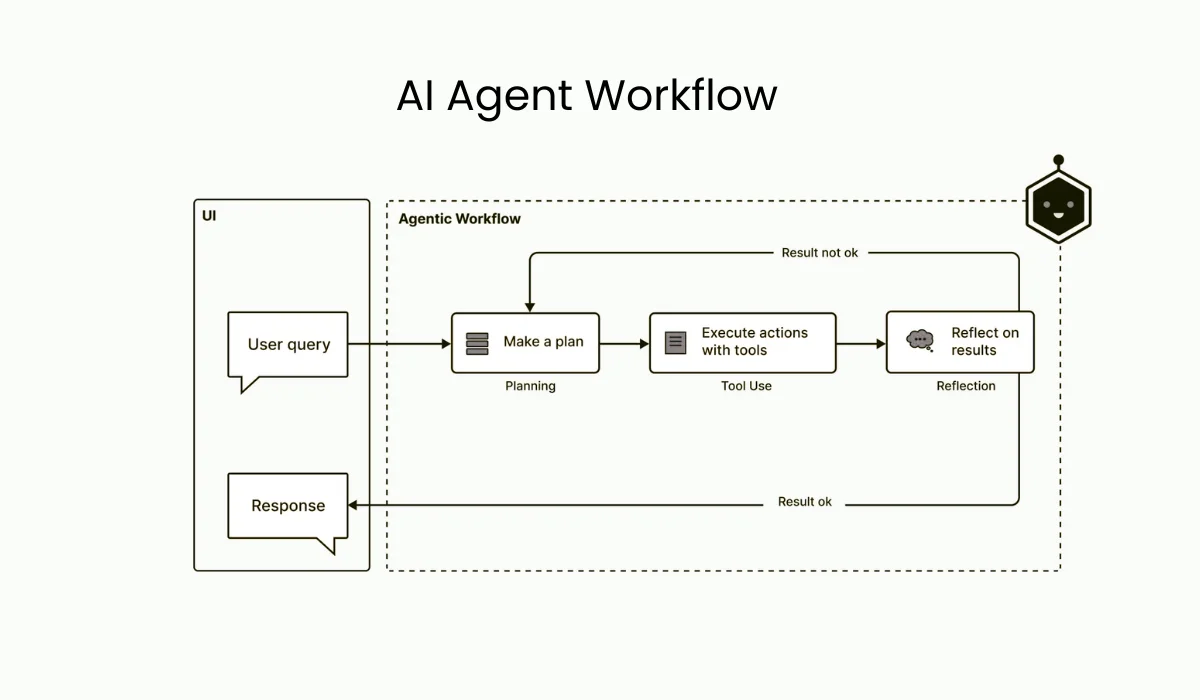
Before we get into designing and optimizing AI agent workflows, it helps to understand what a workflow actually looks like. At its simplest, a workflow has three main parts:
- Input Layer: This is where it all starts, the data, user request, or trigger that sets the workflow in motion.
- Processing Layer: Here’s where the “thinking” happens. The agent analyzes the input, reasons through it, and transforms it into something meaningful.
- Output Layer: Finally, the agent delivers a result, which could be text, a command, an API call, or a decision that feeds into another system.
Workflows aren’t just linear sequences; they involve interactions. An agent might act on its own, collaborate with other agents, or ask for human input at key points. Good workflows make sure everything and everyone works together seamlessly.
Why AI Agent Workflows Matter
AI agent workflows are important because they give structure to how intelligent agents operate. Without a clear workflow, agents can act unpredictably, which can lead to mistakes or inconsistent results. A well-designed workflow keeps everything, data inputs, decision-making, and actions, aligned with your business goals, making AI systems more efficient and reliable.
- Better accuracy and consistency: When agents follow a structured process, they’re more likely to respond correctly across different scenarios and make fewer errors.
- Easier to scale and manage: Clear workflows make it simpler to expand AI systems, monitor performance, and optimize processes as your needs grow.
As AI-driven automation becomes more common, having solid agent workflows is essential. They help maintain control, build trust in your systems, and ensure long-term value for your business.
How to Design Workflow for AI Agents?

Designing a robust AI agent workflow is more than just connecting inputs and outputs. It requires strategic planning and a deep understanding of the task at hand.
- Define the Goal
Every workflow starts with a clear objective. What problem the agent will solve? Ambiguous goals lead to convoluted workflows that fail to deliver reliable results. Whether it’s automating customer support or processing large datasets for insights, defining a concrete goal is the first step.
- Identify Subtasks and Dependencies
Once the goal is established, break it into manageable subtasks. For instance, a document-processing workflow may include:
- Ingesting documents from multiple sources.
- Classifying content by type or topic.
- Extracting key information.
- Summarizing or structuring outputs for downstream use.
Mapping dependencies ensures that each step is executed in the correct sequence and prevents bottlenecks or redundancies.
- Decide on Single vs Multi-Agent Setup
Not every task requires multiple AI agents. Single-agent workflows are good for tightly coupled tasks, while multi-agent workflows improve modularity, efficiency, and scalability when tasks are diverse or complex.
- Map Inputs, Outputs, and Decision Points
Clear data flow is critical. Every input, output, and decision point should be explicitly defined. Consider scenarios like:
- “If input data is incomplete, trigger a fallback process.”
- “If the user’s intent is unclear, ask for clarification before moving forward.”
Great design also incorporates modularity and error handling. By building each step as a standalone unit, you make the system easier to debug. Furthermore, every workflow should have a “Plan B.” If an external API fails, the workflow must have a pre-defined path to recover without crashing the entire session.
Tools for Building an AI Agent Workflow
These AI agent workflow builders help you plan, prototype, and implement the logic of intelligent agents:
- LangChain: For chaining LLM prompts, connecting agents to APIs, and handling reasoning steps.
- AutoGen / Multi-Agent Frameworks: For designing workflows where multiple agents collaborate.
- CrewAI / Role-Based Frameworks: For assigning specific responsibilities to agents and managing interactions.
- Flow-Based Design Tools (e.g., Node-RED, Hugging Face Transformers pipelines): Visual or programmatic workflow design, easy for prototyping.
- Vector Databases (Pinecone, FAISS, Weaviate): For storing embeddings and enabling contextual reasoning in workflows.
Also Read: Why AI Agent Workflows Fail
How to Orchestrate an AI Agent’s Movement and Memory
AI orchestration is all about managing an agent’s memory, state, and communication. Think of it as the “glue” that keeps everything in sync, making sure the AI is doing the right thing at the right time. Without proper orchestration, even well-designed workflows can fall apart.
Techniques for Coordination
- Sequential Execution: Tasks are handled one after the other in a predictable order, like following a checklist.
- Parallel Execution: Multiple agents tackle different parts of a task simultaneously, saving time and boosting efficiency.
- Conditional Branching: The workflow adapts on the fly, changing direction based on what the agent discovers in real time.
Imagine a customer support AI agent. The orchestration layer first sends a query to a Classifier to determine whether the issue is about billing or technical support. Based on that, it pulls relevant information from a knowledge base using Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG). Next, a Writer drafts a response, which is then reviewed by a Critic for quality and safety before it reaches the customer.
This orchestration ensures the workflow runs smoothly, responses are accurate, and tasks are completed efficiently.
Tools for Orchestrating AI Agent Workflows
These tools for AI orchestration manage task execution, coordination, and communication between agents:
- Apache Airflow: Scheduling and automating multi-step workflows; handles dependencies.
- Kubernetes: Deploying, scaling, and managing AI agents reliably in production.
- Prefect: Workflow orchestration with focus on error handling and monitoring.
- Dagster: Another orchestration platform for scheduling, running, and observing workflows.
- ReAct Framework: Combines reasoning with actions for real-time AI task orchestration.
How to Optimize AI Agent Workflow
A working workflow is only the first step. To move to production, you must optimize for speed, accuracy, and budget.
Key Metrics to Track
- Success Rate: Percentage of tasks completed without human intervention or errors.
- Latency: The time it takes for the user to receive a final result.
- Tokens per Task: The computational cost associated with each successful completion.
A Few Strategies to Optimize AI Agent Workflows
- Model Routing: Route simple tasks to smaller, faster models (like GPT-4o-mini) and reserve flagship models for complex reasoning.
- Prompt Engineering: Refine system instructions to improve accuracy without changing a single line of application code.
- Caching: Store responses for common queries to reduce both cost and latency.
- Log Analysis: Use tools like LangSmith or Helicone to trace the agent’s “thoughts” and identify exactly where logic breaks down.
Tools for Optimizing and Monitoring AI Agent Workflows
These help track performance, debug issues, and continuously improve workflows:
- Prometheus + Grafana: Track metrics like response time, task success, and resource usage.
- OpenTelemetry: Observability for distributed AI systems.
- Logging Tools (ELK Stack, LogRocket): Track agent actions and debug errors.
- Experimentation/AB Testing Platforms: Measure performance of different workflow variations.
Common Challenges in AI Agent Workflow Design

Building AI agent workflows isn’t always straightforward. Identifying potential challenges upfront, you build workflows that are smoother, more reliable, and easier to scale. Here are some common pitfalls to keep in mind:
1. Unclear Goals and Requirements
If the objectives of a workflow aren’t clearly defined, agents can produce inconsistent, irrelevant, or incomplete results. Without a clear goal, it’s difficult to measure success, and teams may end up wasting time and resources on tasks that don’t really matter.
2. Overly Complex Workflows
AI agent workflows that have too many steps, branches, or tightly linked processes can slow things down and increase the chance of errors. They also become harder to manage or troubleshoot. Keeping workflows simple and modular helps maintain efficiency and makes them easier to update over time.
3. Poor Data Quality
AI agents rely heavily on accurate and relevant data. Incomplete, outdated, or inconsistent data can lead to wrong outputs, reduce reliability, and make the workflow less effective in real-world applications. Ensuring clean and structured data is critical.
4. Lack of Proper Orchestration
When multiple agents are involved, poor coordination can create overlaps, missed steps, or conflicting actions. Effective orchestration keeps everything in sync, ensuring agents collaborate smoothly and the workflow runs as intended.
5. Limited Monitoring and Visibility
Without proper monitoring, it’s hard to track performance, spot errors, or identify areas that need improvement. Workflows need visibility tools to show what agents are doing, helping teams optimize processes and maintain reliability.
6. Scalability Challenges
Workflows that aren’t designed to grow can struggle with larger workloads, bigger datasets, or more complex tasks. Thinking about scalability from the start ensures the workflow can expand seamlessly without sacrificing performance or accuracy.
Conclusion
AI agent workflows are not just automation; they are structured systems that enable intelligent agents to reason, act, and interact effectively. A successful workflow hinges on three pillars:
- Design: Clearly define goals, subtasks, inputs, and outputs.
- Orchestrate: Coordinate agents, sequence tasks, and integrate with external systems.
- Optimize: Monitor performance, handle errors, and refine workflows for efficiency and scalability.
Even a single, well-executed workflow, such as the customer support agent, can demonstrate the power of structured design, careful orchestration, and continuous improvement. By applying these principles, developers, product managers, and AI practitioners can create intelligent systems that deliver consistent, reliable, and impactful results.






