A machine following predefined instructions can execute tasks perfectly, with minimal errors or deviations. But the moment your workflow changes, you have to rewrite instructions, update the code, and feed it back to the machine. That’s how traditional automation works, efficient for repetitive tasks but rigid when conditions shift.
Many people confuse AI and automation, assuming they’re the same. In reality, they are not interchangeable. AI can learn, adapt, and make decisions, while automation simply follows fixed rules. For businesses exploring process optimization, workflow modernization, or digital transformation, understanding this distinction is key to getting the best results.
This blog covers everything you need to know about AI, AI agents, and automation.
First, the Basics: What Does Automation Mean

Automation refers to the use of technology to execute tasks that are repetitive and do not require human intervention. Here, the rules never change and always give the same outcomes. Generally, there are four main types of automation:
- Basic Automation: Done in a single step and repetitive (e.g., sending scheduled reports).
- Process Automation: Requires multiple steps to complete the process and use many systems (e.g., onboarding a new employee).
- Robotic Process Automation (RPA): Does what humans do and is often used for structured tasks (e.g., invoice processing).
- Cognitive Automation: Has limited intelligence to perform semi-structured tasks (e.g., simple email classification).
With these automation types, you can get reliable, fast, and scalable results; however, if one thing changes in your workflow or process, everything goes to square one.
Why Traditional Automation Works… Until It Doesn’t
Traditional automation has been the backbone of efficiency in enterprises. By handling predictable, rule-based tasks at scale, it frees employees from repetitive work, reduces errors, and accelerates operations. Think of invoice processing, payroll runs, or approval workflows; these are areas where automation consistently delivers results.
But not all automation is created equal. Its effectiveness depends on the clarity of rules and the stability of processes. When conditions change or exceptions occur, traditional automation can stumble. That’s where enterprises often hit a wall; tasks that seem simple in theory become brittle in practice.
When to Use Traditional Automation
- Repetitive Tasks: Activities with clear, structured rules, such as batch processing or routine approvals.
- High Accuracy: Minimal risk of human error when rules are strictly followed.
- Scalability: Can be deployed across multiple systems and departments without additional intelligence.
- Predictable Costs: Implementation and maintenance are straightforward, with little ongoing learning required.
Where Traditional Automation Falls Short
- Lacks Flexibility: Struggles with exceptions or unexpected inputs.
- Limited Context Awareness: Cannot interpret unstructured data like emails, documents, or images.
- No Learning: Unlike AI, it cannot improve performance over time.
- Maintenance Overhead: Complex processes require constant updates if rules or systems change.
Is Robotic Process Automation Same as AI?
No. RPA mimics human interaction with software for structured tasks such as copying data, validating invoices, or logging entries. While it accelerates workflows, it doesn’t learn or adapt. Any unexpected input can cause errors, requiring human intervention. AI agents, on the other hand, bring intelligence, adaptability, and decision-making capabilities that are impossible with traditional automation and RPA.
Also Read: How to Implement RPA in Your Company?
What Are AI Agents?

While traditional automation excels at predictable, rule-based tasks, AI agents are designed for dynamic, uncertain environments. They don’t just follow scripts; they reason, plan, and act autonomously, adapting to new information and unexpected scenarios. This makes them ideal for complex workflows that involve decision-making, unstructured data, or interactions across multiple systems. Therefore, the enterprises are heavily investing in AI agent development to design intelligent systems.
How AI Agents Work
AI agents operate in a loop of perception → reasoning → action:
- Perception: The agent gathers information from multiple sources, including structured and unstructured data.
- Reasoning: It analyzes inputs, identifies patterns, predicts outcomes, and decides the next steps.
- Action: The agent executes tasks, communicates results, or triggers processes, adjusting dynamically as conditions change.
This ability to continuously sense, learn, and act distinguishes AI agents from traditional automation.
What Sets AI Agents Apart
- Dynamic Decision-Making: Can handle exceptions without human intervention.
- Cross-Functional Integration: Works across multiple departments, platforms, or systems seamlessly.
- Learning and Adaptation: Improves performance over time by learning from past interactions.
- Handling Unstructured Data: Processes emails, documents, images, and even voice inputs.
Where AI Agents Are Currently In Use?
Many enterprises are transitioning to custom AI agent services to deploy intelligent agents tailored to their specific operational challenges, ranging from
- IT Operations to monitor networks, detect anomalies, and remediate issues autonomously.
- Supply chain management to forecast demand, adjust inventory, and optimize logistics in real time.
- In customer support, virtual assistants are used to resolve complex queries and escalate issues intelligently.
- For automating report generation, summarizing insights, or assisting with data analysis.
Also Read: What Startups Get Wrong About AI And How to Avoid It
AI Vs Traditional Automation: The Core Difference
Understanding the difference is easier when you compare them across key dimensions. This table highlights the core comparison of AI agents and traditional automation:
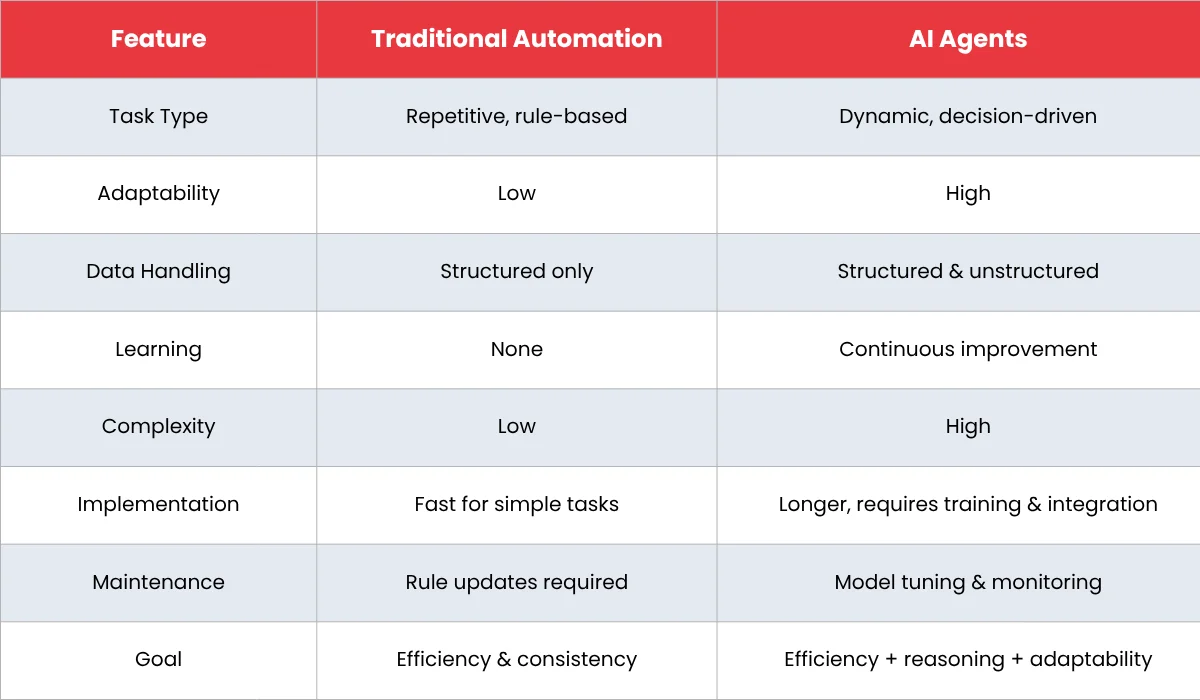
For organizations exploring hybrid workflows, AI agent development enables tailored solutions that complement existing automation systems and handle complex, decision-driven tasks
When to Use Traditional Automation?
Traditional automation is useful in scenarios where processes are stable and predictable, such as payroll, batch processing, or routine approvals. It works best when rules are clear and there’s minimal variation, allowing organizations to achieve quick ROI through fast deployment and low upfront effort.
When to Use AI Agents?
AI agents, on the other hand, excel in dynamic environments like IT operations, supply chain management, or customer support, where tasks require complex decision-making and reasoning. They are particularly effective at handling unstructured data, including emails, documents, images, and inputs from multiple sources, adapting in real-time to changing conditions.
When to Combine Both
Many enterprises achieve the best results by combining traditional automation with AI agents. Automation can handle high-volume, repetitive tasks efficiently, while AI agents manage decision-heavy or adaptive processes that require reasoning and flexibility. For example, an RPA bot might handle invoice entry, while an AI agent validates anomalies and escalates exceptions, creating a seamless, hybrid workflow that leverages the strengths of both approaches.
Conclusion
In the new waves of AI, traditional automation might seem replaceable, but it has long been the backbone of operational efficiency, handling predictable, rule-based tasks with speed and accuracy. AI agents, however, bring intelligence, adaptability, and context-aware decision-making to the table, tackling complex workflows that automation alone cannot manage.
Choosing one over another is not an option. A hybrid approach will be most beneficial where automation handles repetitive, stable tasks, while AI agents focus on dynamic and decision-heavy processes.
Understanding the differences between AI and automation is essential for applying both technologies strategically, future-proofing operations, improving agility, and maximizing efficiency
FAQs
What is the difference between AI and automation?
Automation executes predefined rules to complete tasks efficiently, while AI can learn, reason, and adapt to new situations. AI is designed for tasks that require intelligence and decision-making, whereas automation is best for predictable, repetitive work.
Is automation a type of AI?
No. Automation is rule-based execution, while AI involves intelligence and learning. Automation can integrate AI for more complex tasks, but it is not AI itself.
Which is better, AI or automation?
It depends on the use case. Automation is ideal for predictable, repetitive tasks that follow clear rules, delivering speed and accuracy with minimal human oversight. AI agents are better for complex, dynamic workflows that require reasoning, adaptation, or processing unstructured data. Rather than choosing one over the other, enterprises often achieve the best results by combining automation for routine tasks with AI agents for decision-heavy processes.
Can AI replace RPA?
Partially. RPA excels at handling structured, rule-based tasks, but AI can augment or replace RPA for tasks that require adaptation, processing unstructured data, or decision-making. Often, a hybrid approach is most effective.
Is AI the Same as Simple Automation?
No. Simple automation follows predefined rules without learning. AI can analyze, reason, and adapt to new situations, making it far more versatile than traditional automation.